The Kynex New Issue Pricing Tool
allows you to model a hypothetical security by simply entering the basic terms
of the security.
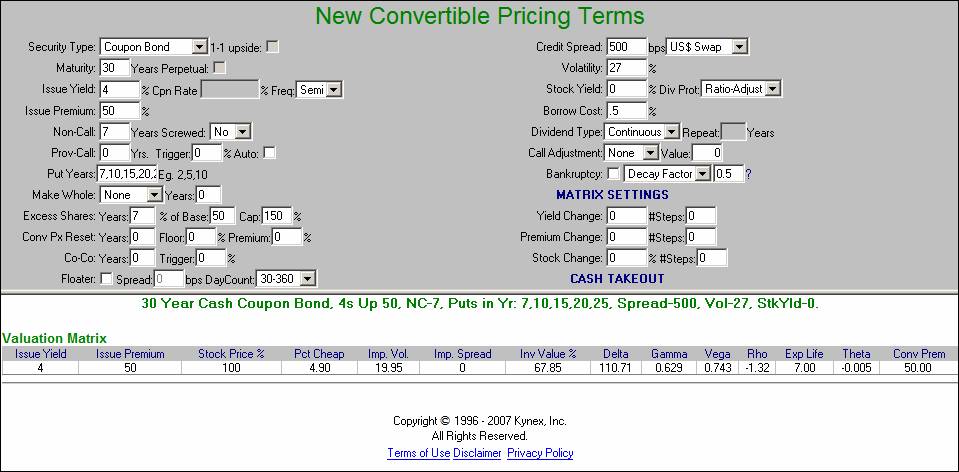
The following details are required inputs for the New Issue Pricing Tool: Security Type, Maturity, Issue Yield, Issue Premium, Call Details (hard call, provisional call, make-whole, and call adjustment), Put Details, Credit Spread Assumption, Yield Curve, Assumed Volatility, Stock Yield, Div Protection Type, Borrow Cost, and Div Type. (See below)
New
Issue Pricing Inputs
Security Type
You have four different options to choose from; Coupon Bond, Accreting Bond, Preferred Stock and Mandatory. A Coupon Bond is a cash coupon convertible bond. Accreting Bonds are bonds that are issued below par and accrete to par or bonds that are issued at par and accrete to redeem above par. The Accreting Bonds can either pay a small coupon or no coupon. Preferred Stock is selected for a convertible preferred stock. The security type Mandatory is modeled as a preferred stock that has mandatory conversion with a classic “DECS” structure. We also model the newer 1 to 1 upside feature which is a variation to the classic DECS structure.
Maturity
The number of years from the issue date that the security
will mature. For example, if the terms
of the instrument indicate a 20 year maturity you would input 20. We allow you to enter fractional years in the
form of a decimal (ex: 10.5 if the maturity is ten years and 6 months from the
issue date).
Perpetual
To indicate a preferred is a perpetual, simply check to the right of the word “Perpetual”. After checking the box, the maturity will appear with the number 30 and a grey background. For more details on the valuation of perpetual securities please click here.
Issue Yield
The issue yield should be the coupon for the security types
Coupon Bond, Preferred Stock, and Mandatory. An example would be a 5% coupon
bond you would input 5 in the issue yield.
For an accreting bond the issue yield should be the rate at which the
bond accretes (also yield-to-maturity). For example, if you had a 0% coupon
bond accreting at 3.5% you would input 3.5 in the Issue yield and 0 in the
coupon rate described below.
Coupon Rate
The coupon rate will only be enabled for Accreting Bonds. For instance if it was a zero coupon bond accreting at 3.5% you would input 0 in the coupon rate. If it pays a coupon of 1% of face, yielding 3.5% to maturity including the coupon you should input a 1.
Issue Premium
The issue premium is the percentage the conversion price will be above the current stock price. Suppose you had a new issue with a 25 percent premium, you would enter 25.
Non Call
The number of years before the security becomes unconditionally or provisionally callable. For instance, if the terms specify non-call 5 then you would input 5. For accreting bonds, the call price is always the accreted value on that date. For non-accreting instruments if the holder is able to put it back on the first call date the generated call price is par; otherwise we generate declining call prices starting above par based upon the coupon, call date and maturity.
Prov-Call / Trigger/Auto
Conversion
The Prov-Call input is the number of years that the security is provisionally callable by the issuer. The Trigger is the percentage above the conversion price where the underlying stock must trade in order for the security to become callable by issuer. Our default assumption is that the stock price must trade above the trigger for 20 out of 30 trading days. For instance, if the security details indicate, “Non-Call 5 and Provisionally Callable for 3 years with a 140% Trigger,” you would input 3 in the Prov-Call years and 140 in the Trigger. If the instrument is provisionally callable from the day it is issued, you must enter 0 as non-call years. By checking the auto conversion box, the model assumes that the issuer must call (as opposed to might call) the security if the stock price exceeds the trigger.
Put
The number of years from the issue date when the bonds are put-able at the option of the holder. The New Issue Pricing Tool assumes all puts are at par or the accreted value if the security is an Accreting Bond. If the security has puts in multiple years, the years should be separated by a comma. For instance, if the bonds are put-able in years 5, 10, 15 and 20 you would enter 5,10,15,20.
Make Whole
The make whole feature gives the holder an additional amount of cash if the security is called by the issuer between dates specified in the indenture.
You can select from one of three choices:
None – the model will ignore the make whole feature
Coupon – if called the issuer will pay the holder the coupon amount in dollars multiplied by the number of years specified in the box to the right less coupons already paid
Premium – if called the issuer will pay the holder the point premium on the day the security was issued less coupons already paid
This feature is usually linked with the provisional call feature in the market.
Excess Share
To set up a new convertible with a variable conversion ratio (aka embedded warrants) you must enter the number of years that the excess shares are applicable, the number of additional warrants as a percentage of the base conversion ratio and the cap as a percentage of the base ratio. If there is no cap, please enter 100 plus number of warrants as a percentage of base. (If the terms indicate that the Cap = Par / Reference Stock Price (fairly common in the market), then please enter 100 plus Issue Premium %).
Conversion Price Reset
To value a convertible security that features a Conversion Price Reset please input the years, floor, and premium. The years will be the number of years from the issue date when the reset event takes place. The floor is entered as a percentage and indicates the minimum level the conversion price can be reset to, in regards to the original conversion price. A reset premium is when the conversion price gets reset downward and then is multiplied by the reset premium to come up with the new conversion price. The reset premium is usually the issue premium. If there is no reset premium then input “0” in the Premium % field.
Co-Co
The Co-Co feature has two inputs. The number of years the Co-Co is effective
and the trigger price. For bullet bonds,
please note, that if the number of years matches the maturity years then the
Co-Co trigger will be applicable on the maturity date and screw the investor at
certain stock price levels. For example
if you have a 5 year bullet bond, and input the Co-Co years as 5 and the
trigger as 120, this is interpreted as the bond holder will not be allowed to
convert the notes at maturity if parity is below 120. The investor gets screwed for parity levels
of 100-120 where they would have converted and collected parity but now are
forced to get Par. To avoid the investor
getting screwed on the maturity date, please make the Co-Co years 0.1 less than
the maturity years. For
this example make the Co-Co years 4.9.
Floater
To price a new floating rate convertible security you will
need to check the floater box, input the spread over the relevant yield curve,
and choose the desired Day Count. The
spread will be applied on the relevant point on the curve based on the coupon
frequency chosen. For example, if the payment frequency is quarterly, the
spread will be applied on the 3-month rate. The spread for the floating rate
convertible can be negative.
Credit Spread
The assumed spread in basis points over the chosen yield curve for valuation. The spread is determined by the company’s credit worthiness.
Curve
The yield curve you choose to value the convertible security
with.
Volatility
The risky volatility used to value the convertible security.
Stock Yield
The stock yield is the annual dividend of the underlying stock divided by the current stock price. The stock yield is a required input when using continuous dividends.
Div Prot
You can select from one of three choices:
None – the model will ignore the dividend protection feature and will make no adjustments for dividends paid by the company on the underlying stock
Ratio Adjustment – the model will make adjustments to the conversion ratio when dividends are paid above the dividend anchor amount, using the standard conversion ratio adjustment formula (See Ratio Denom)
Pass-Thru – the model will pass thru a cash amount to the convert holder equivalent to the amount of dividend above the dividend anchor amount (See Cash Pass Thru)
For more information on Dividend Protection, please refer to the March 2006 and June 2006 bulletins.
Borrow Cost
Finance Rate – Rebate Rate
Where the Finance Rate is the rate which your broker charges you to finance the convertible and the Rebate Rate is the rate used to calculate the rebate on your short-sale proceeds.
Div Type
You can choose either Continuous
or Discrete for your dividend assumption.
For definitions of the dividend types see the glossary. For an
example on how to properly enter discrete dividends in Kynex, see the discrete schedule example in this document.
Grey Market
You could input the grey market level as a percentage of
issue price. We will calculate the implied volatility
and implied spread based on this level.
Call Adjustment
To value a security using call adjustment parameters, enter Parity + in the Call Adjustment drop-down box and enter the percent above parity in the box to the right indicating that the bonds will not be called by the issuer unless parity over the call price as a percentage exceeds the given amount.
Bankruptcy
Check the box next to bankruptcy to turn on the bankruptcy
mode. Click for more details.
After entering the
details of the security and clicking the submit button, Kynex will output the
results in the following format.
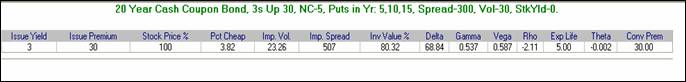
Cash Takeout
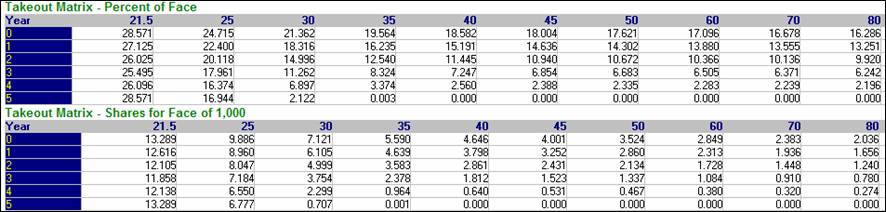
Kynex provides the ability to generate a Cash Takeout Make-Whole Matrix for new issues. Kynex generates a percent of face matrix and a number of additional shares matrix given years and stock prices. In the years field, enter a whole number representing the number of years from issue that you would like the matrix to be generated. The number of years cannot exceed the number of non-call years plus the number of prov-call years. (If the security is non-callable for 3 years and provisionally callable for 2, then the maximum number of years the matrix will be generated is 5 years from issue.) Next, enter the stock prices you would like the matrix to include separated by commas, e.g. 21.5,25,30,35. The first stock price is assumed to be the reference stock price to generate the matrix.
Here is an example of
the takeout make-whole matrices. The
number of years from issue is represented vertically and the stock prices,
horizontally. Year 0 represents the
issue date and year 1 represents one year after the issue date.
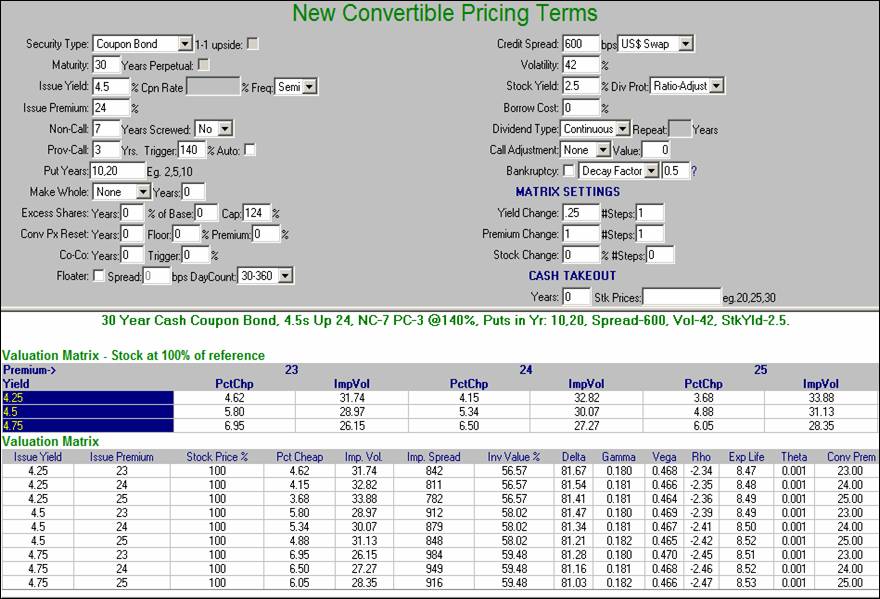
New Issue Pricing Tool Example:
The New Issue Pricing Tool allows you to model multiple scenarios at the same time. This feature is useful for new issues coming to market where the terms of the structure are not finalized.
For instance, consider the following terms for a pending new convertible security.
·
· Premium Range 23-25%
· Maturity 30 Yrs
· Non call 7 Yrs Provisional Call 7-10 Yrs @ 140% Trigger
· Put Yrs 10, 20
· Full Dividend Protection Via Conversion Ratio Adjustment
· We will use a 600 Spread over US Swap Curve and 42 Vol for valuation
To view all possible scenarios within the price talk, the first step is to enter the terms of the structure into the appropriate fields using the mid-points of the price talk. Using the Matrix Settings, you can specify the variation in coupon and premium by entering the amount of change from the midpoint you would like to see. In this case .25 for the coupon and 1 for the premium. The # Steps field will tell the New Issue Pricing Tool how many steps from the mid-point to value, where 1 step is + and – the amount of change for the coupon and premium. If you were to enter a Stock Change scenario in the Matrix Setting for 1 step Kynex will show you scenarios only where the stock declines.
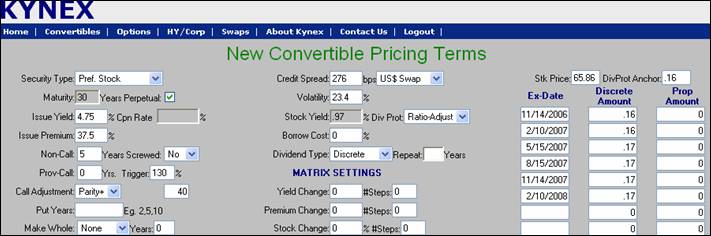
New Issue Pricing Tool Example:
The New Issue Pricing Tool allows you to value a discrete dividend schedule, call adjustment parameters, and perpetual convertible preferred stock.
For instance, let us look at a perpetual preferred using the call adjustment parameters and discrete dividends.
· Coupon 4.75%
· Premium 37.5%
· Non call 5 Yrs Provisionally Callable for life @ 130% Trigger
· Div Protection Via Conversion Ratio Adjustment
· Discrete Divs .16 per quarter increasing to .17 after two quarters
· Call adjustment of Parity + 40%
· Stock Price at Issue $65.86
· We will use a spread of 276 bps over US Swap Curve and a 23.4 Volatility
Perpetual
To indicate a preferred is a perpetual, simply check to the right of the word “Perpetual”. After checking the box, the maturity will appear with the number 30 and a grey background. For more details on the valuation of perpetual securities click here.
Call Adjustment
To value a security using call adjustment parameters, enter Parity + in the Call Adjustment drop-down box and enter the percent above parity in the box to the right indicating that the bonds will not be called by the issuer unless parity over the call price as a percentage exceeds the given amount
For this example we assume the company will not call the security unless parity is greater than 140%.
To enter a discrete dividend schedule, select the Dividend Type as Discrete. After doing so the discrete dividend schedule interface will appear to the right. The discrete schedule should be entered in the same manner as the discrete schedule on the convertible details page. The DivProt Anchor is usually the reference dividend amount when the convertible is issued. The anchor is used in the adjustment formulae for conversion ratio adjustment and pass thru dividend protection valuation. It is very important that you specify the Stock Price as well as the DivProt Anchor. The DivProt Anchor and discrete schedule should reflect the dividend payment frequency of the stock.
New Issue Pricing Tool
Example
The New Issue Pricing Tool allows you to value a convertible bond with Excess Shares and a Contingent Conversion feature.
For example, a new convertible bond is announced with the following terms:
Maturity 30 years
Coupon 4%
Premium 50%
Non-Call 7 years
Puts 7,10,15,20,25
Excess Share 50% of the base ratio (until Call date)
Cap No